Jinda Han
CS PhD @ UIUC | ML @ Apple | MS&E @ Stanford
HCI & AI Researcher in Fashion & Social Media
CS PhD @ UIUC | ML @ Apple | MS&E @ Stanford
HCI & AI Researcher in Fashion & Social Media
About Me
Currently, I'm working at Apple and part-time studying MS&E in SCPD at Stanford. Previously, I obtained my Ph.D. in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). I was advised by Professor Ranjitha Kumar in her Data-Driven Design Group @ Interactive Computing (IC/HCI) Lab. I also worked closely with Professor Hari Sundaram and Professor Li Zhao.
Prior to my Ph.D. journey, I received my B.S. and M.S. degrees from the (same) Department of Computer Science at the UIUC, where I worked with Professor Chengxiang Zhai in his Text Information Management and Analysis Group (TIMan) @ Data and Information Systems (DAIS) Lab.
Besides, I have worked (or intern) at some companies such as Apple (2021-present, 2019, 2018), eBay (2020), SEDAC (2017), Synopsys (2016), Accenture (2014), etc. In addition, I served as the Web Co-Chair of ACM GROUP in 2020 and as the Chair of ACM SIGGRAPH at the UIUC chapter from May 2015 to May 2016 What's more, before I came to US, I was an opera singer (see "Hai gia vinta la causa" in 2008).
Experience
Over 10 years of experience in research and development in AI and HCI, including Large Language Models (LLMs) such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), graph-based computing, alignment and memory, as well as machine learning, social network analysis, social computing, large-scale data mining, information retrieval, natural language processing, and human–computer interaction. These technologies have been applied across domains such as fashion, social media, advertising, e-commerce, and intelligent agents for trend prediction, recommender systems, and more.
Core Research & Technical Skills
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), alignment, memory, graph-based computing
- AI & Big Data: Applied Machine Learning, Deep Learning, NLP, Large-Scale Data Mining, Social Network Analysis, Social Computing, Data Visualization, Information Systems
- Human-Centered Computing: Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Intelligent Agents, Trend Prediction, Recommender Systems
- Full-Stack Web Development: React, Angular + Node.js, Flask/Django, PHP (LAMP), RESTful APIs, MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL
- Mobile Development: React Native (Android/iOS), Swift (iOS), Java (Android)
- Tools & Platforms: AWS/GCP, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face, Apache Spark, Git, Docker, Kubernetes, etc.
Teaching
- CS598DM: Data Mining Capstone (Instructor: Reza Farivar and Chengxiang Zhai)
Summer 2021, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- CS598rk: HCI for Machine Learning (Instructor: Ranjitha Kumar)
Spring 2021, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - CS498rk: The Art of Web Programming (Instructor: Deniz Arsan)
Spring 2020, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - CS598rk: HCI for Machine Learning (Instructor: Ranjitha Kumar)
Fall 2019, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - CS498rk: The Art of Web Programming (Instructor: Ranjitha Kumar)
Spring 2019, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - CS598rk: HCI for Machine Learning (Instructor: Ranjitha Kumar)
Fall 2018, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - CS498rk: The Art of Web Programming (Instructor: Ranjitha Kumar)
Fall 2017, Teaching Assistant, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Conference Important Dates
- A.ACL 2026. Deadline: 1/5/2026
- A.WWW 2026. Deadline: TBD (soon)
- A.SIGIR 2026. Deadline: TBD (soon)
- A.IJCAI 2026. Deadline: TBD
- A.NeurIPS 2026. Deadline: TBD
- A/B.EMNLP 2026. Deadline: TBD
- A/B.NAACL 2026. Deadline: TBD
- B.CIKM 2026. Deadline: TBD (25 passed)
- A.ICML 2027. Deadline: TBD (26 passed)
- A.KDD 2027. Deadline: TBD (26 passed)
- A.MM 2026. Deadline:
- A.CSCW 2026. Deadline:
- A.CHI 2027. Deadline:
- B.GROUP 2026. Deadline:
- C.DIS 2026. Deadline:
- B.CogSci 2026. Deadline:
- C.IEEE BigData 2026. Deadline:
Research Projects
Current Projects (Outdated)
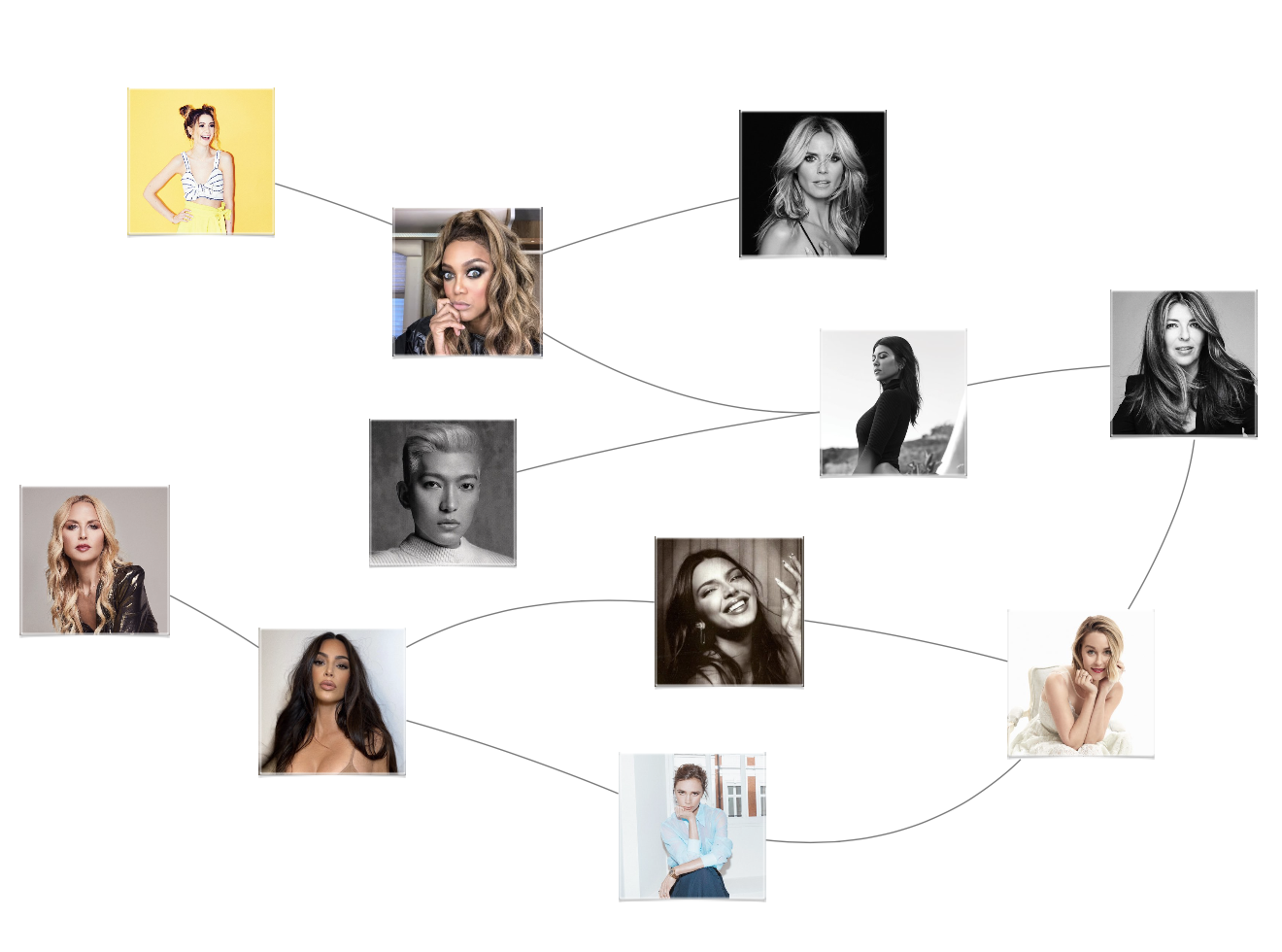
Mining Fashion Influence on Social Media
The rise of social media has changed the nature of the fashion industry. Influence is no longer concentrated in the hands of an elite few: social networks have distributed power across a broader set of tastemakers. To understand this new landscape of influence, we created FITNet — a network of the top 10k influencers of the larger Twitter fashion graph. To construct FITNet, we trained a content-based classifier to identify fashion-relevant Twitter accounts. Leveraging this classifier, we estimated the size of Twitter’s fashion subgraph, snowball sampled more than 300k fashion-related accounts based on the following relationships, and identified the top 10k influencers in the resulting subgraph. We use FITNet to perform a large-scale analysis of fashion influencers, and demonstrate how the network facilitates discovery, surfacing influencers relevant to specific fashion topics that may be of interest to brands, retailers, and media companies.
- Mining Fashion Influence on Social Media University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. 2023.
- FITNet: Identifying Fashion Influencers on Twitter (Dataset available at http://fashioninfluence.net/fitnet) Jinda Han, Qinglin Chen, Xilun Jin, Weikai Xu, Wanxian Yang, Suhansanu Kumar, Li Zhao, Hari Sundaram, and Ranjitha Kumar. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction (PACM HCI). CSCW 2021.
- Identifying Fashion Accounts in Social Networks Doris Jung-Lin Lee, Jinda Han, Dana Chambourova, and Ranjitha Kumar. KDD Workshop on ML Meets Fashion. 2017.
Previous Projects
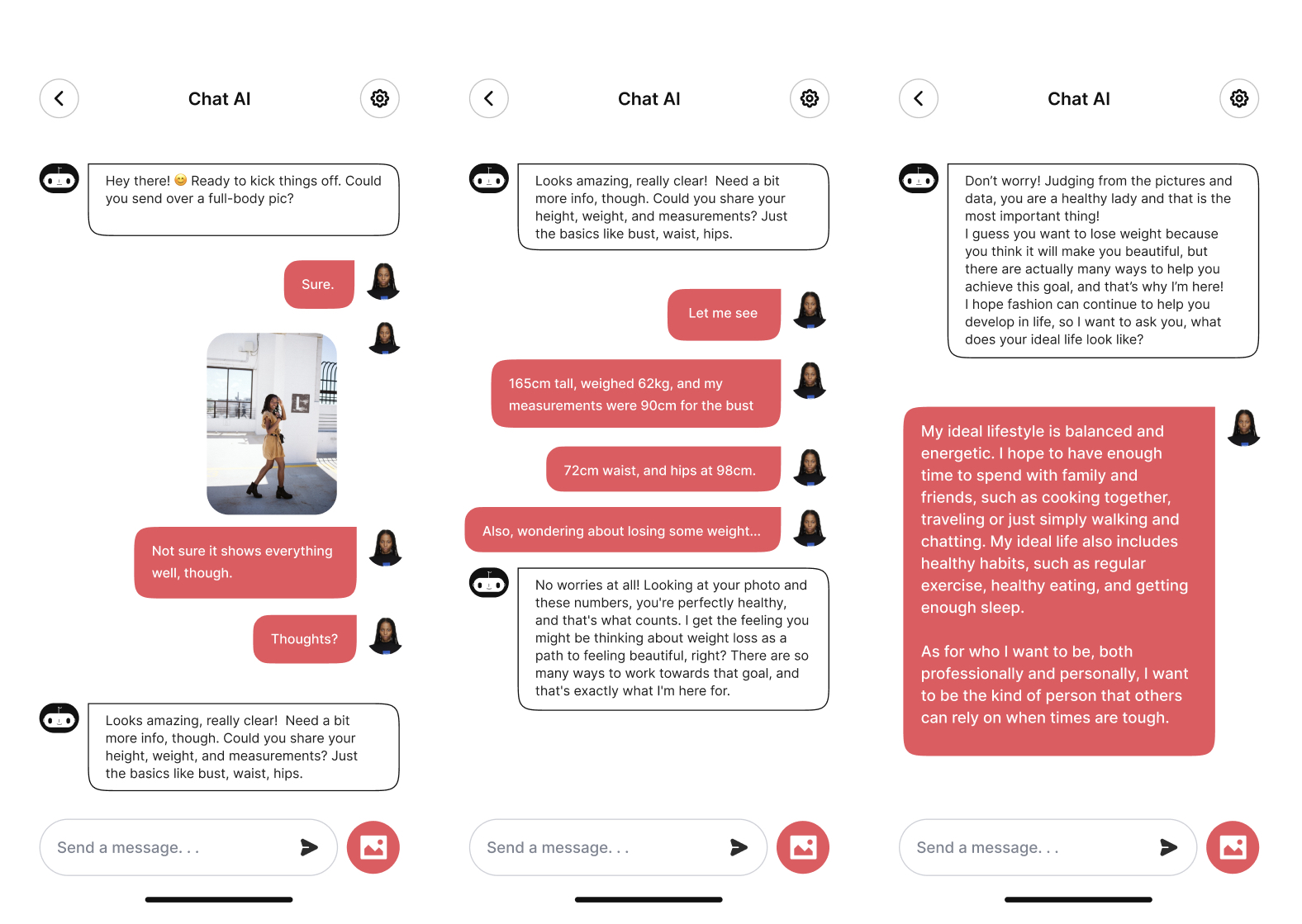
Fashion Stylist Chatbot
Fashion serves as a means to not only present an enhanced version of oneself but also to actively become a better individual through its influence. Meanwhile, the rapid development of AI technology has brought more possibilities in the tech-assisted personal fashion domain. We review the literature regarding imitation theory, fashion psychology, and the changes in fashion paradigms. Leveraging these theories, we propose a future personalized fashion solution: a fashion stylist chatbot that is capable of generating inspirational fashion styles on virtual representations of our bodies. Differentiating from previous work, this solution can help us build our wardrobe starting from thinking about our psychosocial aspects.
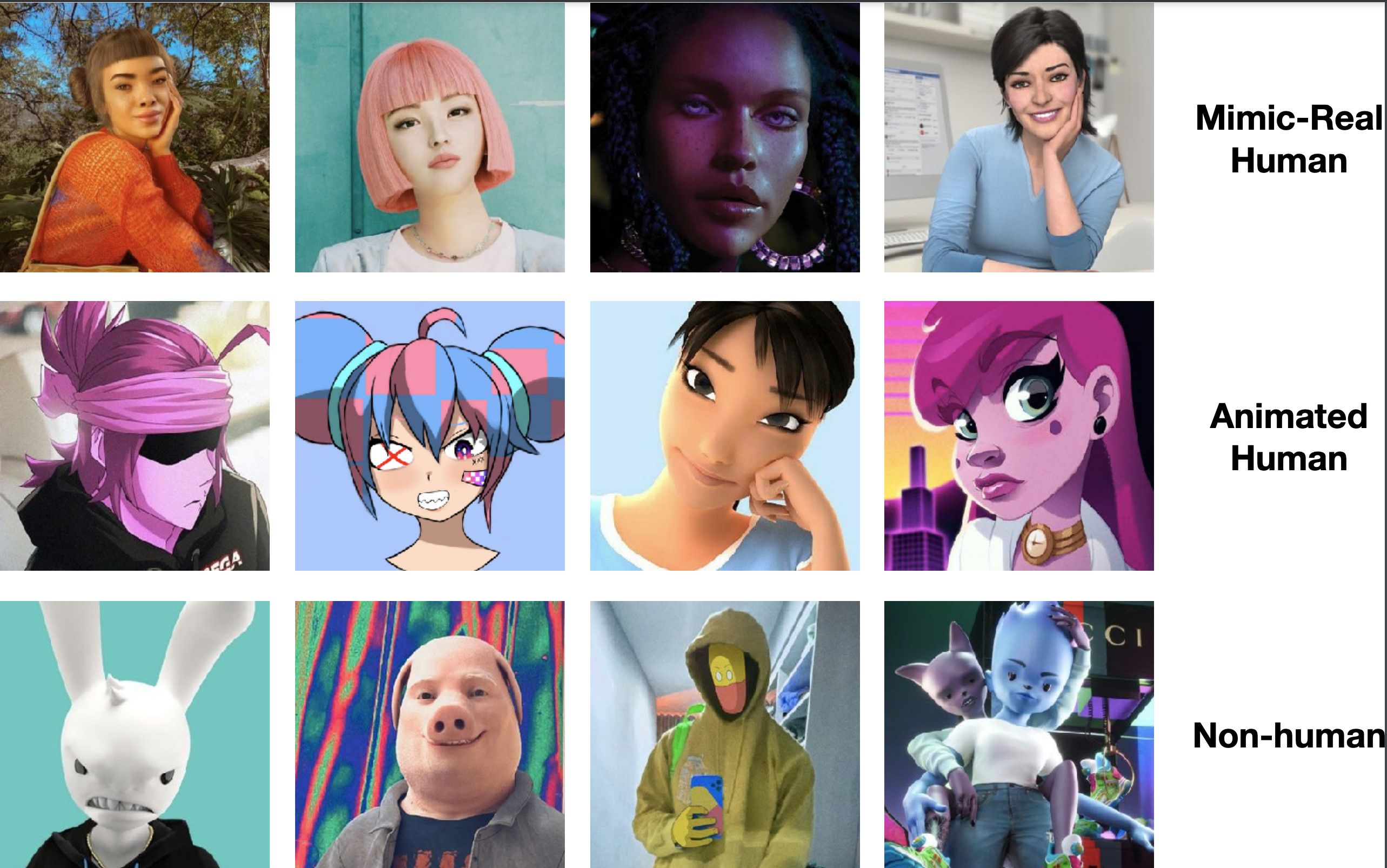

Virtual Influencers on Social Meida
Virtual Influencers (VIs) are computer-generated characters, many of which are often visually indistinguishable from humans and interact with the world in the first-person perspective as social media influencers. They are gaining popularity by creating content in various areas, including fashion, music, art, sports, games, environmental sustainability, and mental health. Marketing firms and brands increasingly use them to capitalise on their millions of followers. Yet, little is known about what prompts people to engage with these digital beings. In this paper, we present our interview study with online users who followed different VIs on Instagram beyond the fashion application domain. Our findings show that the followers are attracted to VIs due to a unique mixture of visual appeal, sense of mystery, and creative storytelling that sets VI content apart from that of real human influencers. Specifically, VI content enables digital artists and content creators by removing the constraints of bodies and physical features. The followers not only perceived VIs' rising popularity in commercial industries, but also are supportive of VI involvement in non-commercial causes and campaigns. However, followers are reluctant to attribute trustworthiness to VIs in general though they display trust in limited domains, e.g., technology, music, games, and art. This research highlights VI's potential as innovative digital content, carrying influence and employing more varied creators, an appeal that could be harnessed by diverse industries and also by public interest organisations.
Fashion Style Recommendation Engine
Used deep learning to train the fashion model by using the latent fashion concepts jointly in two languages capturing these elements and styles. Optimized search engine backend with new data from ecommerce and ezine fashion websites. Output personalized dressing combo recommendations based on style, similarity, etc.

Predicting Fashion Choices Using Unimportant Domains: Personality vs Fashion Questionnaire Systems
Recently, in light of the current emphasis on security and privacy, people have become more aware of the data that companies gather from them. However, companies need this data to create recommendations that will be useful to their customers. Our idea is to develop knowledge of a person’s preferences using data that does not gather sensitive information such as viewing or buying history. Many people already take fun quizzes on Facebook and other web platforms to learn more about themselves, so why not take the answers collected from these quizzes instead? In this project, we aim to connect answers to fun questions such as “What would you rather do on a Saturday morning?” and “Which instrument would you like to learn?” to choice of fashion styles.
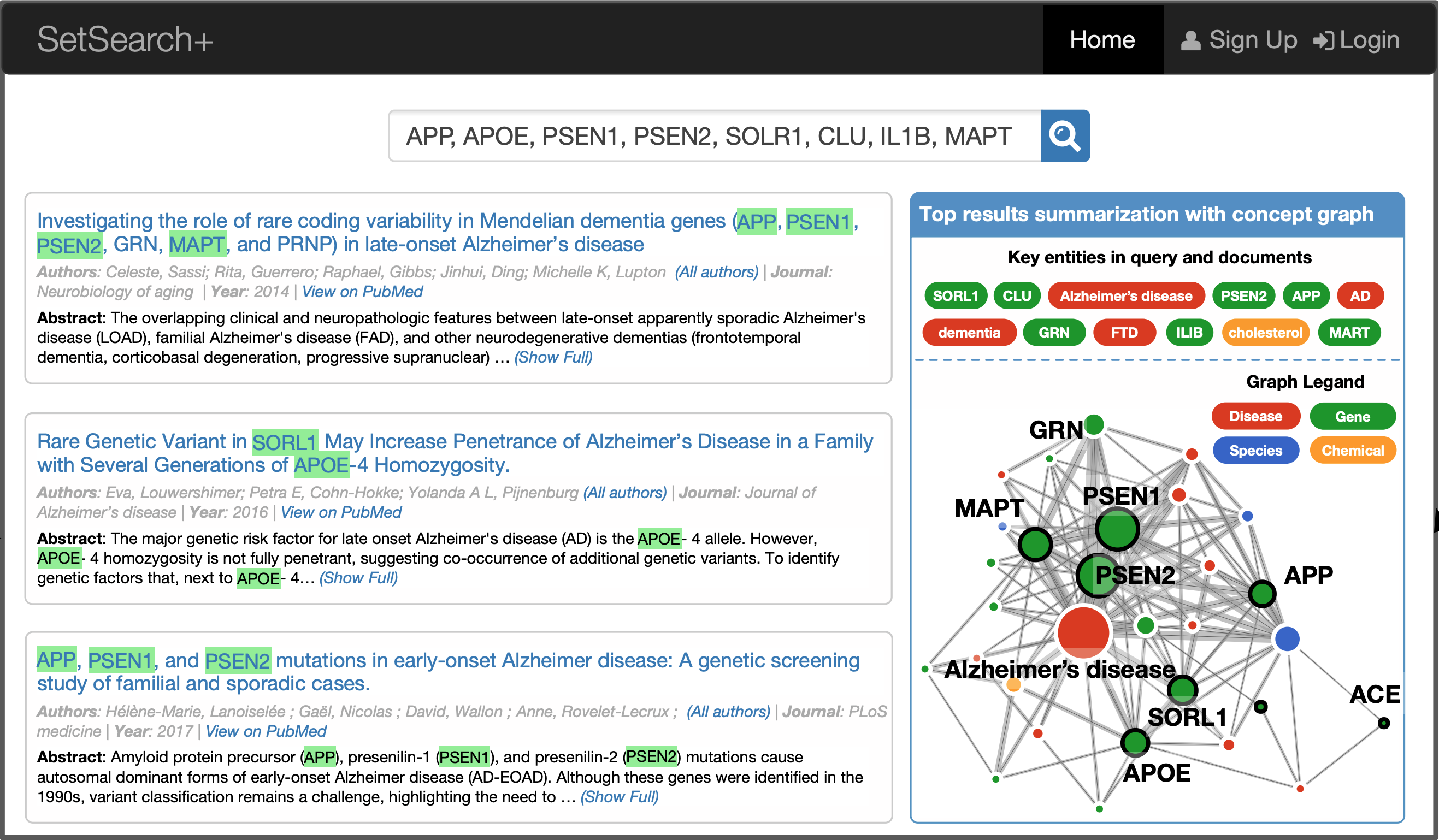
Large-scale Study on Heterogeneous Information Networks
SetSearch+: Web System 1, Web System 2
- A Constrained Maximum Likelihood Estimator for Unguided Social Sensing Huajie Shao, Shuochao Yao, Yiran Zhao, Chao Zhang, Jinda Han, Lance M. Kaplan, Lu Su, Tarek F. Abdelzaher. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM). 2018
- SetSearch+: Entity-Set-Aware Search and Mining for Scientific Literature Jiaming Shen, Jinfeng Xiao, Yu Zhang, Carl Yang, Jingbo Shang, Jinda Han, Saurabh Sinha, Peipei Ping, Richard Weinshilboum, Zhiyong Lu and Jiawei Han. In The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. KDD 2018 Demo Track
- HighSim: Highly Effective Similarity Measurement in Large Heterogeneous Information Networks Huajie Shao, Jinda Han, Sida Li. Manuscript. 2016.
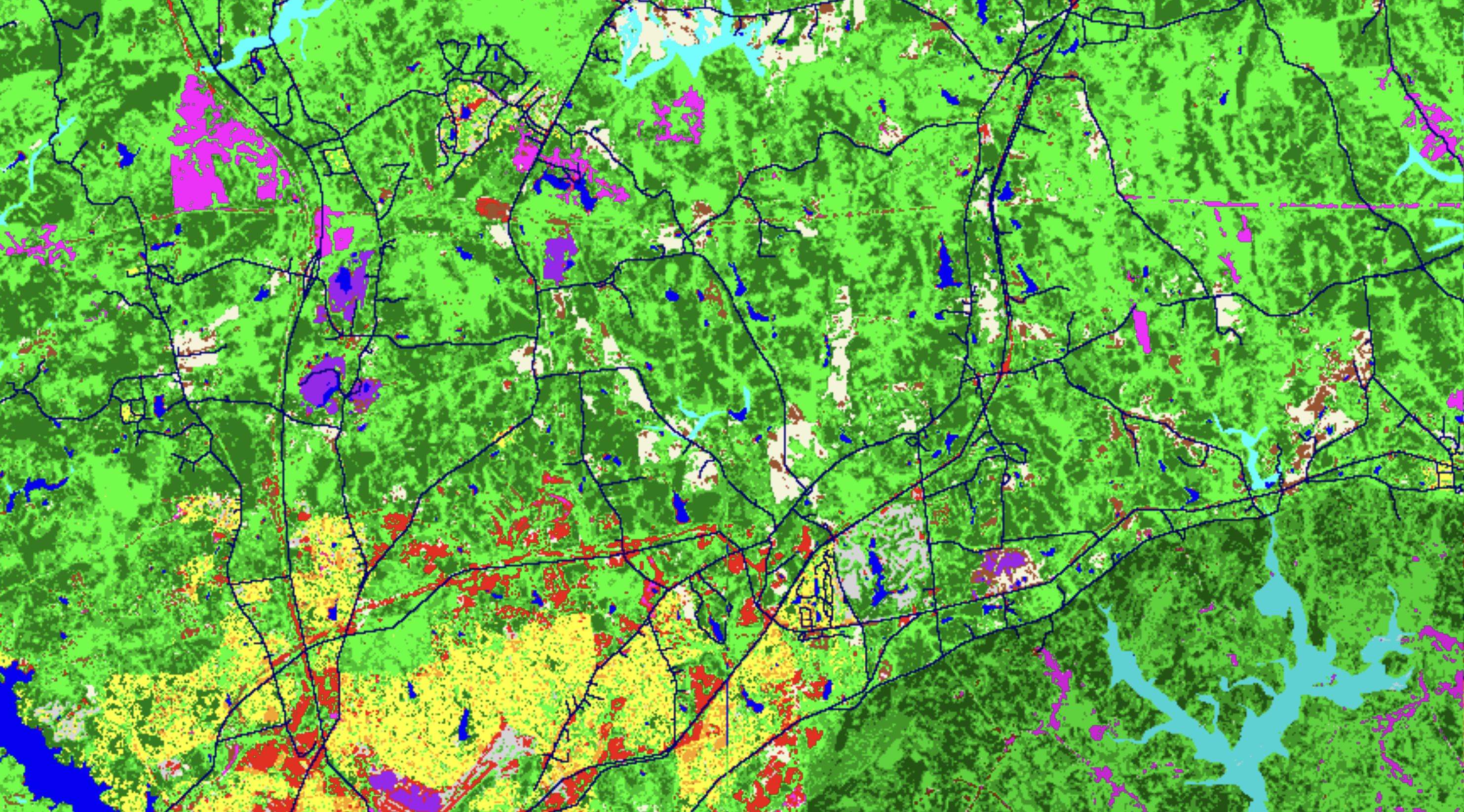
Landuse Evolution and Impact Assessment Model
"Better tools are needed to manage regional dynamics, not just as economic systems or static inventories of resources, but as complex systems that are part of regional and global networks. However, effective management requires both that we understand the systems to be administered and that we understand the implications of our strategies. We have attempted here to outline an approach for understanding the dynamics of urban systems and the potential implications of urban policy and investment management decisions. We described one modeling approach — LEAM — that utilizes cellular automata and other technological advances in spatial simulation modeling to help improve a community’s ability to make ecologically and economically sound decisions. LEAM was intended to enable users to capture stochastic influences and view the reported probable consequences of intended events in a scenario-based format that is comprehensible by local experts, decision-makers, and stakeholders. The LEAM Model, its development, and its application to several regions within the continental United States is conducted and managed by a team of faculty, staff, and students at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This team brings together expertise in substantive issues, modeling, high-performance computing, and visualization coming from the departments of Landscape Architecture, Urban Planning, Geography, Economics, Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA), the United States Army Corp of Engineers, and private industry. The mission of the LEAM group is to help others understand the relationships between human economic/cultural activities and biophysical cycles from a changing land use perspective. All of us must realize that these interacting systems behave in very complex and dynamic ways. Understanding the extent of how one system affects another will allow us to make better land use management decisions in the future."
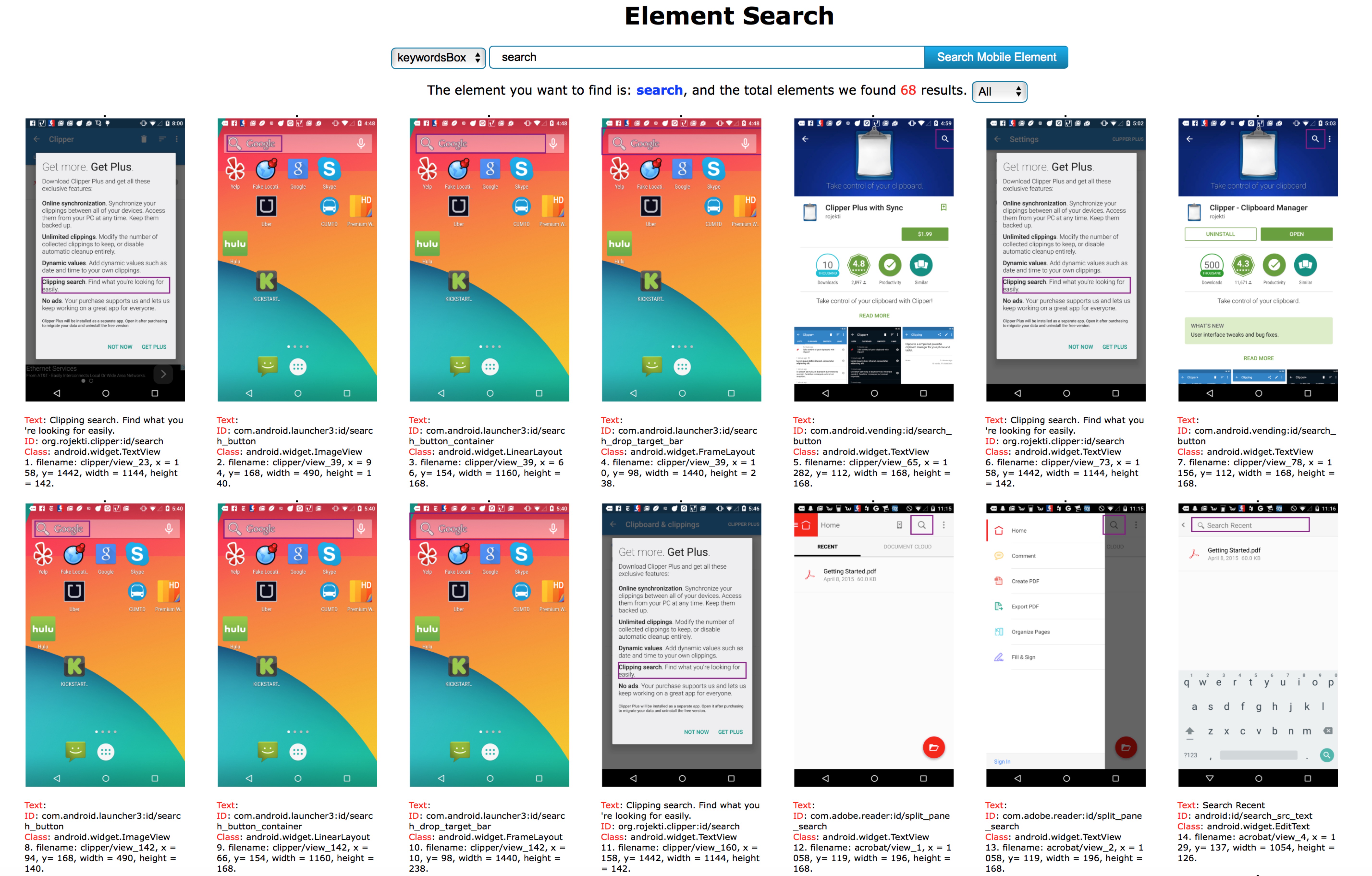
Mobile Element Search Engine
[Search Engine Demo]
Identify the elements and icons on Android UI, enable the basic search function to categories these elements.

Virtual Reality For Personal Interior Design
[floor plan mining demo]
Mining the floor plans on the web, and the goal was to generate the floorplan layout design into a 3D model automatically.
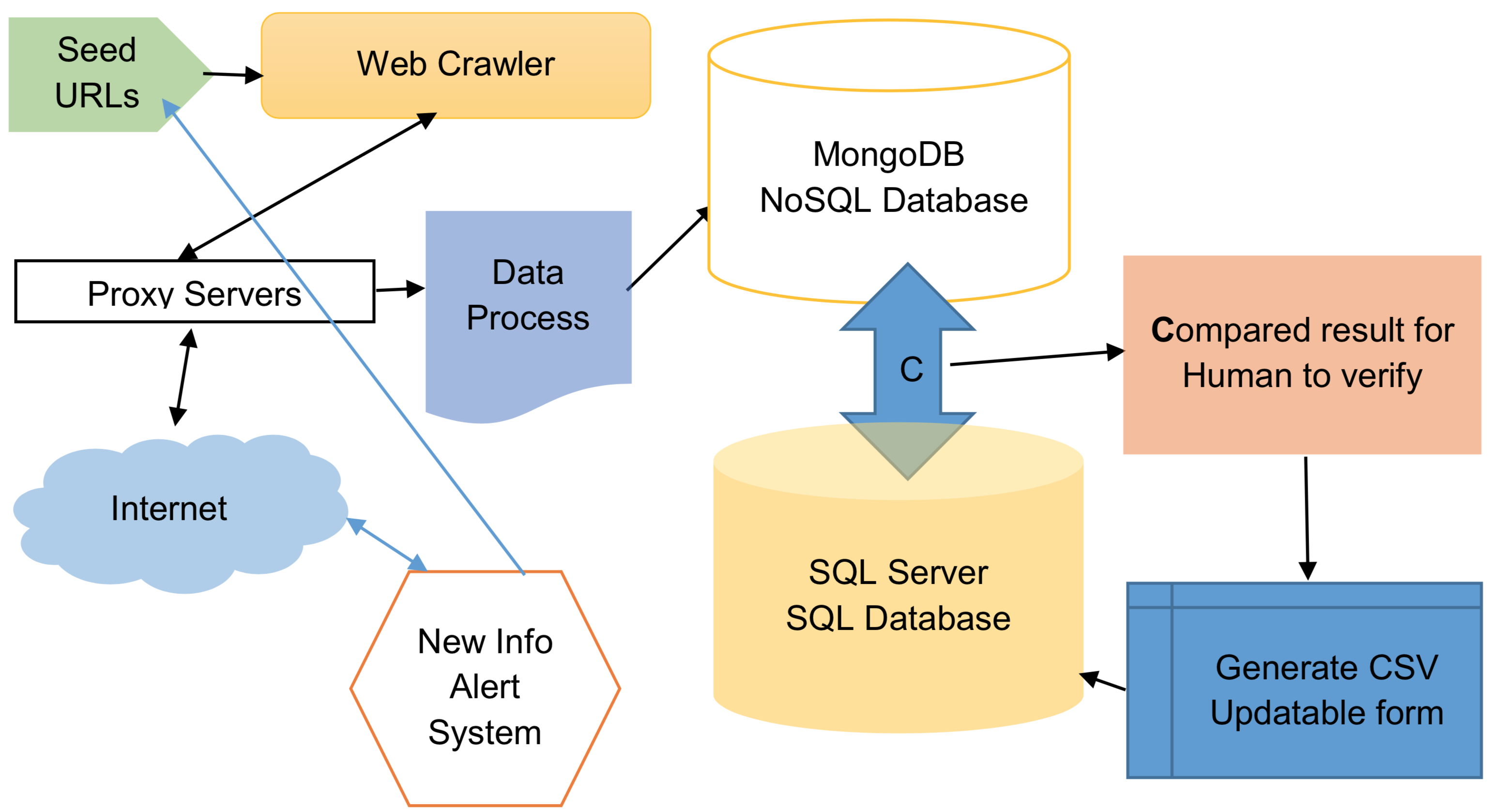
Enterprise Information Update and Alert System
Many companies today require a system to gather valuable online information about products or customers. With such a system, they can improve their products or services based on this information, thereby enhancing overall company performance. Receiving a large volume of accurate information is the first crucial step in this process, followed by storing and retrieving the data. The next step involves comparing this data with the existing system database to update outdated information. Finally, future predictions and automatic updates via alerts represent the last essential stage. Currently, there is limited research on how to build such a system. In this work, I propose an Update and Alert System (EIUAS) to help companies maintain their product databases. The system includes several components: a web crawler, data extractor, data verifier, data integrator, dynamic database design, data retrieval engine, update checker, prediction module, and alert system. This system enables companies to gather relevant product or customer information from public sources. To evaluate its effectiveness, we calculate the update percentage. Additionally, a qualitative assessment by a domain expert confirmed the system's usefulness and its capability to handle dynamic, updatable information.

Intelligent Medical Diagnosis System
The work presents an intelligent online medical diagnosis system designed to help users identify possible diseases based on their symptom descriptions. Unlike general-purpose search engines, this system provides more accurate and structured health information by leveraging a curated database of over 4,000 diseases. It incorporates a custom-built search engine that uses BM25L scoring and Rocchio feedback to rank relevant diseases based on symptom similarity. Users can refine results using filters like age, gender, race, and diagnostic methods (e.g., CT, MRI), and the system includes a user account feature to track search history and feedback. The system also features a user-friendly web interface developed with HTML, CSS, PHP, and Java backend components. Evaluations using Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) show that the system provides highly relevant results for most queries. However, current limitations include strict keyword matching and difficulty handling misspellings or complex medical terminology. Future improvements include incorporating stemming, enhancing data quality, adding NLP features, and optimizing performance with caching and compression techniques.
Misc. & tools
Before 2014, I also built some random stuff in various areas:
